Welding cable is the specialisation type of cable made for use in the welding application. It features a single bare annealed copper conductor, that is standard for extreme flexibility. The cable is typically used in welder leads and power supply applications, including high flexibility, offering several benefits, high-temperature resistance and durability.
When it comes to fundamental characteristics of welding cables, flexibility and consistency have the most impact on how effective they are in operation. A welding cable must possess sufficient strength to withstand physical wear and tear, which would otherwise lead to its insulation becoming compromised during welding processes. However, it should also be bendable for use by the welder without any possibility of permanent deformation.
What is Welding Cable?
Welding is an art, and like any craft, it requires the right tools and materials. One crucial component often overlooked is the welding cable size chart. This chart serves as a roadmap, guiding welders to select the appropriate cable size for their projects. We go further into the intricacies of welding cable size charts in this article, providing guidance and insight to enable welders of all skill levels.
Measure Your Welding Circuit Length
Measuring the length of your welding circuit is the most important thing to do to get the right welding cable. Power source, electrode cable, work cable, anything else you have. Calculate the total length of the electrode and work cables.
Copper Core vs Aluminum Core Welding Cable
The middle of a welding cable carries hundreds of layers of electrical conductors which include copper or aluminium. As the strand remembers of the centre increases, the power in addition to the conductivity of the cable increases. Thus, the centre of a welding cable immediately affects its performance in numerous welding jobs.
Different Types Of Welding Cable Insulations
As for the outdoors, the insulation of the welding cable is likewise as critical as its core, if not more. This insulation layer is what prevents contact of the centre with surrounding gadgets which can cause electrical incidents. Therefore, shopping for a cable with first-rate insulation coating is important, particularly for heavy-duty jobs. The three most widely used insulating coatings for welding cables are PVC, Neoprene, and EPDM. Out of which, EPDM and Neoprene are favoured alternatives.
EMPD and neoprene provide high flexibility and ruggedness. Thus, you may count on those cables to have a protracted shelf existence with a dependable insulation capacity. This coating also can maintain outside problems like abrasion and dirt without any substantial damage to the insulation layer. PVC on the other hand gives high-quality resistance to outside cuts or wear and tear. The most effective problem with PVC coating is the dearth of flexibility which is critical in loads of welding jobs.
What Cable Size Should You Choose?
Moving on, another important factor that should be considered is the size of the welding cable. It is dependent on numerous factors the size of the welding cable you should have when you need it for your work. When you have to choose a welding cable size, the first thing that needs to happen is for you to calculate how many amperes will be required in this specific welding operation, bearing in mind that the length of the cables should also not be forgotten along with the duty cycle of your machine.
While numerous expert welders believe that the dimensions of the cable are suffering from its duration, it isn’t the entire tale. Instead of simply the length, you may have to not forget the whole welding circuit earlier than finalizing the welding cable size. It additionally consists of some elements that are generally ignored consisting of welding leads, floor clamps, holders, and so forth.
Choose the Correct Cable Size:
To find the recommended cable size based on the calculated load, voltage drop, and cable length, use cable sizing charts or tables.
Make sure that the chosen cable size complies with all applicable safety regulations and requirements.
Consider Voltage Drop:
Calculate the voltage drop across the cable with the use of the voltage drop method. This is essential to make certain that the cable can cope with the required modern-day without excessive voltage loss.
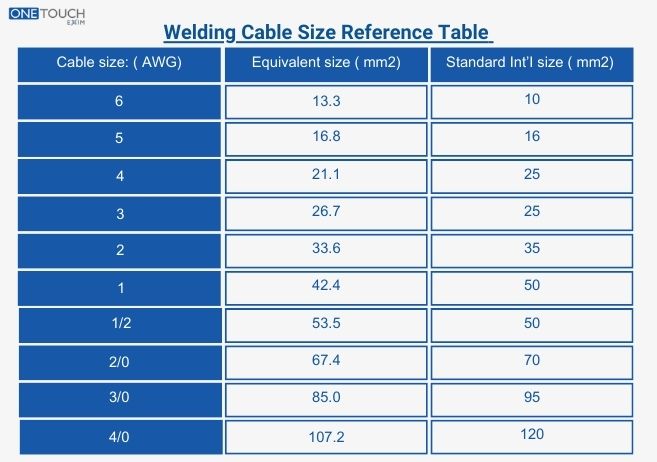
Welding Cable Reference Table
Indeed, you have probably realized the significance of selecting the proper size and length of the welding cable for the job. Whereas you may have more flexibility using a lengthy wire whose thickness is relatively smaller for a heavy-duty project, dangers arising from burns and electrical short circuits far outstrip the benefits associated with the same. Equally important, when running on a high amperage level, an electric current passing through your body would lead to the death of any welder at any given time.
Cable size: Metric Cross-Sectional Area
| Cable size: ( AWG) | Equivalent size ( mm2) | Standard Int’I size ( mm2) |
| 6 | 13.3 | 10 |
| 5 | 16.8 | 16 |
| 4 | 21.1 | 25 |
| 3 | 26.7 | 25 |
| 2 | 33.6 | 35 |
| 1 | 42.4 | 50 |
| 1/2 | 53.5 | 50 |
| 2/0 | 67.4 | 70 |
| 3/0 | 85.0 | 95 |
| 4/0 | 107.2 | 120 |
The Concept Of Welding Cable “Ampacity”
The concept of welding cable “ampacity” refers to the maximum amount of electrical current that a cable can safely conduct. This is also known as the cable’s “amperage capacity” or “current capacity. The ampacity of a welding cable is crucial for ensuring both safety and optimal performance in welding packages.
What is Ampacity?
Ampacity, which translates to “amperage capacity,” is the highest electrical current that a cable is capable of conducting without causing damage. Consider it to be the “power limit” of the cable.
Why Ampacity Matters
Getting the ampacity right is crucial for two main reasons:
- Safety: An overloaded cable poses a safety issue, as was covered in the dangers section.
- Performance: Inappropriate ampacity might impair your weld quality and eventually cause harm to your equipment.
Extension Cables
Welding cables and extension cables function similarly. Basically, for the desired length of the extension cable, you need a cable that can withstand the input voltage and amperage of the welder.
Conclusion
Choosing the proper welding cable size is critical for ensuring efficient and safe welding operations. By considering elements including wire gauge, modern potential, duration, responsibility cycle and welding type, and the usage of a cable length chart, welders can choose the correct cable size for their specific projects. Additionally, the right care and maintenance of the cables are critical for their sturdiness and safety.