People use metal for various purposes in their daily life. When you are selecting items made of metals, it is crucial to know the characteristics of the metal and how long it could be used. You would not be able to choose the best metal for your particular demands, if you do not know what components the metal required for your product and other uses.
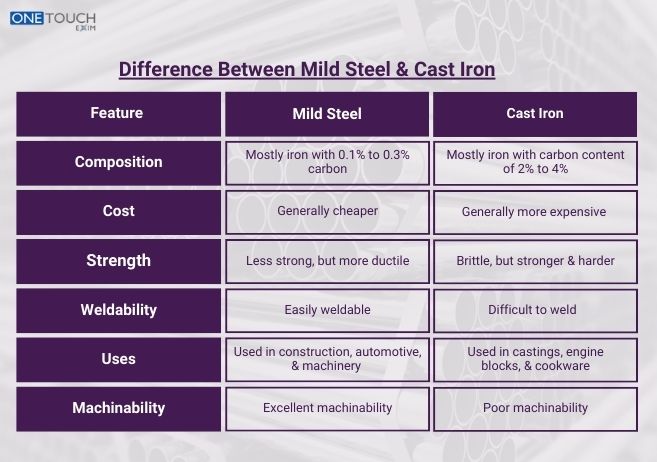
Out of all metals, mild steel and cast iron are the most prevalent and commonly used metals. Both of them are used for manufacturing heavy items and construction. They come under different properties which are also suitable for many applications. In this blog, we will learn the primary differences between mild steel and cast iron in terms of properties, strength, cost, uses etc. Let’s check out.
Difference Between Mild Steel and Cast Iron
So, here we have provided the comparison list of mild steel and cast iron. They are as follows:
1. Overview
Mild Steel
Mild steel is an iron-carbon alloy, means it is made of iron and carbon. It is also known as soft steel or low-carbon steel or plain carbon steel, because it contains less amount of carbon content. Due to its versatile properties, it is widely and commonly used materials in number of industries.
Mild steel’s machinability property allows it to be shaped, drilled, cut and welded easily. It also includes the welability property, which makes it a favorite material for manufacturing companies. It can be melted down and reused to make new items. It is also consider as a ferrous metal because of its high iron content and magnetic properties.
Cast Iron
Cast iron is also an iron-carbon alloy, which contains more amount of carbon. It is best known for its hardness and brittleness which makes it resistant to deformation and wear. The surface of cast iron can be protected by different means like painting and coating, making it prone to corrosion and rust.
Cast iron’s heat retention feature maintains a constant temperature and evenly distributes heat which is ideal for manufacturing cookware utensils like dutch pans etc. Unlike mild steel, it can also be melted to remove impurities and can be reused. Cast iron is often used in wide range of applications including machines, pipes and many more.
2. Properties
Mild Steel
Mild steel contains 99% of iron and carbon content of 0.05%-0.30%. The percentage of carbon increases the melting point around 1400°C of this steel by strengthening the bonds between the iron atoms and other alloying elements.
Mild steel is not only composed of iron and carbon, but also with several components that makes it widely used. For instance, sulfur, phosphorous, chromium, cobalt and manganese. Mild steel is a type of fibrous structure.
Due to mild steel’s less carbon content, it is less prone to hardness or brittleness and exhibits high ductility and malleability which can be shaped easily without cracking or breaking. Addition of alloying elements in the mild steel may improve its wear and corrosion resistance. However, compared to other metals, this steel has poor vibration dampening.
Cast Iron
Cast iron has the higher carbon content as compared to mild steel. Approximately, it contains 2% to 4% of carbon which plays a crucial role in its properties. It is comprised of other elements like magnesium, sulfur, manganese, silicon, nickel, chromium, cerium, molybdenum and so on.
The melting point of cast iron is lower as compared to mild steel, typically around 1200°C. It possess properties of good vibration dampening which is used for making beds for machine. Heat treatment and microstructural modifications may improve the ductility and malleability of this alloy.
Cast iron is considered as an excellent thermal conductor. It is a type of granular and crystalline structure with grayish or whitish tinge. This metal is a brittle material and it can be solidified by sudden heating and cooling process.
3. Strength
Mild Steel
The strength of mild steel can be measured in two types. First, the tensile strength, which means the capability of load or stress it can withstand until cracks, stretches or breaks. Second, the compressive strength meaning before falling under compression, the amount of load it tends to reduce it size.
So, the ultimate tensile strength of mild steel is 400-550 MPa (Megapascal) and the compressive strength is 200-250 MPa. When it comes to greater tensile strength, mild steel is the best choice.
Cast Iron
The strength of cast iron in terms of compressive strength is higher ranging from 630 to 710 MPa. While, the tensile strength varies, but the approximate is around 295 MPa.
This alloy has better compressive strength which provides greater resistance against breaking and provide long term durability.
4. Castability
Mild Steel
In terms of castability, mild steel is better in this feature. The amount of less carbon present in this steel, makes it more ductile and less hard, allows it to cast into different and complex shapes. It is suitable for both casting and forging.
Cast Iron
When it comes to cast shapes out of the material, cast iron is the best choice. Due to high carbon content, its fluid molten state is easier to cast them in complex shapes in heavy and large objects.
5. Corrosion Resistance
Mild Steel
Mild steel is lower in terms of resistance to corrosion and it can also rust easily when it is exposed to oxygen, moisture, humidity and water. So, to overcome this issue in steel, a protective layer of coating is applied on the surface of mild steel. This coating prevents corrosive substances and moisture.
It can also achieved by various means including galvanizing, when the surface of the mild steel is exposed to moisture the zinc element reacts with oxygen to form oxide layer that shields steel from corrosion. Certain surface treatments like chromating and phosphating may create a thin layer to protect the steel’s surface from corrosion.
Cast Iron
Cast iron is more corrosion resistance alloy as compared to mild steel. The high amount of carbon present in this iron, makes it less prone to corrosion and the silicon provides an oxide layer that protects and shields the surface to enhance its corrosion resistance.
In addition, cast iron also contain graphite that acts as a protective layer and reduces the electrochemical reactions which prevents from corrosive ions that leads to corrosion.
6. Uses
Mild Steel
Mild steel is considered as versatile material and is used in a wide range of applications. Some of them are as follows:
A) Construction: Due to tensile strength and various properties of mild steel, it is used in construction projects including roofing, cladding, railings, fencing, bridges, beams, columns, roads, highways. It is also used in construction equipment like bulldozers, cranes etc.
B) Tools and Machinery: Mild steel is used in manufacturing hardware tools like pliers, screwdrivers, wrenches etc. Machinery components like bearings, shafts, gears and so on.
C) Automotive Industry: Mild steel’s excellent ductility and weldability, it is used in engine and transmission components like cylinder heads, engine blocks, oil pans and sump plates. Components like axle, suspension seat frames, fender and wheel, and many more is used for manufacturing.
D) Cookware: It is also used in cookware. However, some grades of cookware is not durable.
E) Pipelines: Mild steel is commonly used in pipeline of oil and gas industry for the distribution of natural gas, crude oil and so on. It is also used in power generation, chemical processing, sewage system etc.
Cast Iron
Cast iron is used in various applications such as:
A) Agriculture Machinery: This iron produces a wide range of agriculture components. For instance, gearboxes, reducers, frames and chassis for tractors, plows, harrows, cultivators, cradles and others.
B) Utensils: Cast iron exhibits excellent durability, heat retention and non- stick properties which is ideal for baking, seasoning and frying foods. It is used in making of utensils like pots, dutch oven etc.
C) Construction: It is used in constructing iron beams, columns and many more.
D) Tools: Cast iron is also used in manufacturing of various tools including axe heads, hammers etc.
7. Cost
Due to lower energy requirements and material costs, cast iron is cheaper than mild steel, while mild steel may be expensive because of its manufacturing process and use of prefabricated forms.
However, the cost may differ in different regions and suppliers may offer different rates according to the global demand.
Conclusion
In the end, it is essential to consider material’s properties before deciding between cast iron and mild steel. Mild steel is ideal for using in constructions and automotive applications, since it is softer than cast iron but still have enough strength and is easy to form into different sizes and shapes. However, cast iron has a larger carbon content than other elements, as it is perfect for heavy-duty equipment.
Therefore, before choosing between these two materials, you have to think about your particular demands!