In the world of production, there are many ways of manufacturing that one can opt for. Metal casting is used in several industries. Its uniqueness makes it an ideal choice for a wide range of industrial sectors. Here in this blog, we will explore more about steel casting process methods, processes, and applications.
What is Steel Casting Process
Steel Casting is the manufacturing process and different kinds of steel are used in this process. In the steel casting process, molten steel is poured into a cast to form a desired shape. It is usually used where cast iron is insufficient in the required strength. In other words, Cast steel casting is used in applications where strength is of uttermost importance.
Properties of Steel Casting Process
Cast steels have varying physical properties that can change when heat or other chemicals are added to the process. The cast steel will undergo careful selection and processing to ensure it meets the required output. Some properties are required for the steel casting process are:
1. Hardness
Metal casting is resistant to abrasion and has a high degree of hardness that prevents even scratches from being visible in the material.
2. Toughness
Cast steels are capable of withstanding stress. To improve the toughness of cast steels, alloying metals and applying heat can be used.
3. Strength
Deformation of cast steel by force is a challenge because of its strength, which also determines its durability.
4. Wear Resistant
Cast steels can withstand wear and tear, friction, and frequent use. Their wear resistance levels are ideal for components that will be used frequently.
5. Rust Resistant
The material’s corrosion resistance is due to this. Even with constant use, cast steels exhibit a high level of tolerance for elements that can cause corrosion.
6. Ability to be Welded
Cast steel has an advantage over other castings because it can be welded to create the shapes and forms needed without any damage.
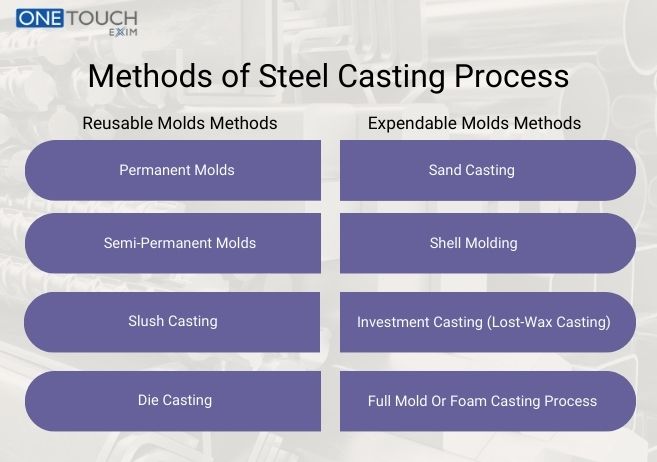
Methods of Steel Casting Process
There are various types of steel casting Processes. However, there are some of the major steps of the steel casting process. Metal casting comes within two main categories i.e. processes with reusable molds and another one is processed with expendable molds.
1. Reusable Molds Methods:
It is utilized with materials having low melting point. Therefore, metal alloys can be cast in reusable molds without having any issue. Casting processes require heat, such as making cast-iron products, which can compromise the structural integrity of the mold over time.
Permanent Molds:
Metals that have a higher melting point than the metal they are filled with are typically used to make permanent molds. The pouring of fluid metal is done without any external pressure. Simple permanent cores are required to be withdrawn for reuse from the finished casting. These molds are sometimes used in the process of iron casting, as well as with lower-temperature alloys.
Individual operations, such as placing the cores, coating the mold, closing the mold, pouring, opening the mold, and ejecting the casting, are performed as each mold passes through the next stations. First-time molds are preheated before the casting is poured so that it does not crack due to the difference in temperature. This form of molding is durable to be used with iron, but it is not a preferred style for yellow brasses.
Semi-permanent Molds:
It is because the cores used in the casting process might be expendable sand cores. The complex core shapes are possible with sand cores because they do not need to be extracted intact from the final casting. If the casting is left to remove cores, they can be “shaken out” with vibration, to drain like sand through an hourglass. The density, tolerance, and appearance advantages of permanent mold casting exist only in the section cast against the metal mold.
Slush Casting:
This type of casting style creates hollow castings without needing cores by merely coating the inside of the mold with a small amount of metal, creating a metal “skin”. There are different ways to approach slush casting depending on the speed of the metal or other material sets. In this method, the founder can fill small amounts of the liquid into a mold and rotate the metal to cover the steel from the inside. In another, the founder can fill the mold completely and then pour excess material out after a specified cooling time. Zinc, aluminum, and pewter are metals that are commonly slush cast.
Die Casting:
The process of die casting involves pouring molten metal into a mold cavity under high pressure. The mold cavity is created by using two hard tool steel dies which have been moulded into shape and work similarly to an injection mold during the process. Zinc, copper, aluminum, magnesium, lead, pewter, and tin-based alloys are commonly used in die castings. Depending on the type of metal being cast, a hot-chamber machine or a cold-chamber machine is used.
2. Expendable Molds Methods:
Expendable mold methods are best for the casting of ferrous metals. These are cost-effective because they do not have to be dominant for the high temperatures involved. The methods are discussed below:
Sand Casting:
It is a manufacturing process in which molten metal is filled with the sand mold containing a hollow cavity in the desired shape. After some time, the casting cools and solidifies. Then the poured sand is broken and shaken out. Casting materials for sand casting include epoxy, concrete, metal, plaster, and clay.
Shell Molding:
It is a casting process used to produce metal parts. The mold is composed of resin-infused sand that gives the product a high-quality surface finish and good dimensional stability. Shell molding products are common in piston engines for parts like valves, camshafts, and gears.
Investment Casting (lost-wax casting):
It is also known as precision casting or lost-wax casting, and is a manufacturing process in which a wax pattern is used to shape a disposable ceramic mold. The item to be cast is shaped into a wax pattern, and then coated with refractory ceramic material.
Full Mold or foam casting process:
The full mold or foam casting process is a joint mixture of sand and investment cast processes. A foamed polystyrene pattern is used in this type of casting. Using a gating and runner system, the foamed pattern can be finished, and the draft allowance can be eliminated. Sometimes the pattern is removed before filling, but with some foams, the pattern can be left in place in the mold to instantly vaporize when heated.
Applications of Steel Casting Process
Steel castings are more effective in many applications. Therefore, it has become more in demand in the market and still growing worldwide.
1. Railway Locomotives:
Steel castings are used in many of the essential components of railway locomotives. They can be found in components such as side frames, wheels, couplers, and bolsters.
2. Construction Equipment:
The building and construction industry needs tools and equipment that can withstand high stress and pressure. So, cast steels are the perfect method for making construction equipment and components such as wheels, load wheels, and many others.
3. Mining Equipment:
The mining industry is vulnerable. Everything that is utilized in its operations must be robust and competent to provide worker safety. Carefully crafted steel casting is used to make the equipment required by the business.
4. Power Station Apparatus:
The thermal and nuclear power stations use steel casting to ensure durability and efficiency. The properties that possess steel make it a reliable component in this industry.
5. Agricultural Machines:
Many agricultural machines go through very harsh conditions and this makes the steel casting very easy.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the metal casting process requires specialized tools and equipment with a lot of creativity. Metal castings are important for industrial purpose because of their efficiency.