Steel tubes, tubing, and pipes perform important functions in a variety of sectors. And are essential components in a variety of applications. Because of their exceptional strength, durability, and flexibility. These cylindrical steel structures are critical in industries such as construction, manufacturing, infrastructure, and transportation. Stainless steel manufacturers utilize an original manufacturing process. It typically begins with the selection of high-quality steel alloys with great mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and the capacity to withstand high temperatures. These alloys are then formed into seamless or welded tubes using procedures like extrusion, piercing, or rolling.
Steel Pipes
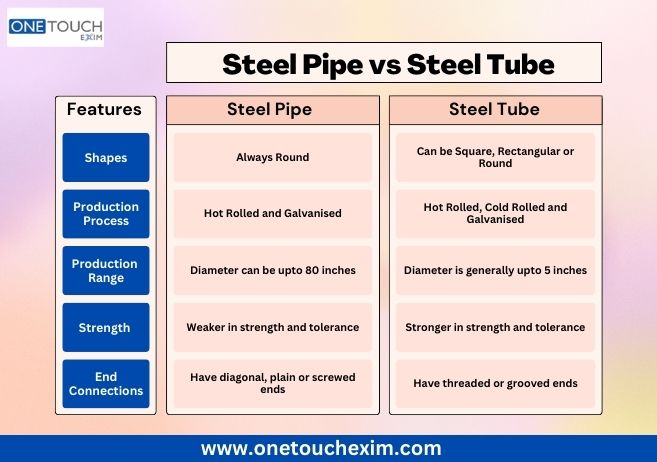
Steel pipes are strong and long-lasting pipes made of iron and other metals like aluminium or manganese. They are seamless or may be welded along the length of the pipe. They are zinc-coated for corrosion resistance using a hot zinc bath or an electroplating process. Because zinc is non-toxic to humans, it is ideal for coating water pipelines.
Steel pipes are extensively utilized in the transfer of water and gas. They are available in a variety of diameters ranging from 3/8 inch to 2 inch. Working with steel pipes can be difficult since they must be threaded. Despite its strength, steel may rust over time. This occurs when the zinc coating on the interior of the pipe deteriorates due to continual contact with water, resulting in corrosion.
Benefits of Steel Pipe
Corrosion is the most common problem in construction but steel pipes are the best choice to avoid corrosion and make greater strength because these pipes are rust-proof. It can last for many years. It is also environmentally friendly. You spend less when you use steel pipes because these are durable. These pipes also help to reduce wastage. Give strength and versatility and even gives you good thermal installation performance.
Steel Tubes
Tubing is a term for hollow components that might be round, square, rectangular, or oval in shape. They have a variety of uses, including pressure equipment, mechanical applications, and instrumentation systems. Steel tubes are made from a variety of materials, including iron, carbon, manganese, vanadium, and zirconium. Tubing can be manufactured in two ways: seamless or welded.
A seamless tube is created by rolling a solid piece of steel into a circular form. It is then perforated and stretched to its full length. Consider forming a play dough cylinder and stretching it by inserting your finger into the center. This procedure, however, is carried out using machines that use heat and spinning.
Benefits of Steel Tubes
They are known for their superior corrosion resistance properties. These are very useful for construction areas where humidity, moisture, and corrosion substances are present because they are highly resistant to rust, and oxidation even in harsh environments.
Steel tubes are sustainable because it is recyclable and using recyclable steel tubes in construction helps to maintain resources and reduce waste. These steel tubes are hygienic and easy to clean.
They have great strength because they are hollowed, rust-proof steel tubes that have constant thickness and diameters and cross-sectional shapes throughout the length.
It has the ability to transport cold or hot liquids and gases.
Difference Between Steel Pipe and Steel Tube
Steel pipe and steel tube have different characteristics that differentiate them from each other:
Manufacturing Process: Steel pipe is manufactured from a single piece of metal, whereas steel tube is made by welding or other ways of putting many pieces of metal together.
Applications: Steel pipe is widely used to transfer fluids or gases, making it appropriate for sectors such as oil and gas, plumbing, and irrigation. Steel tube, on the other hand, is frequently used in structural applications such as building frameworks, supports, and frames for machinery and equipment.
Diameter: Depending on the intended usage, steel pipe is available in a variety of diameters ranging from small to big. Steel tube, on the other hand, is often smaller in diameter and is more commonly utilized in situations where structural strength is a significant requirement.
Cost: Because of the differences in production techniques and intended applications, steel pipe is often more costly than steel tube. The price difference is determined by criteria such as size, grade, and quantity required.
Leakage Potential: When properly built and maintained, steel pipe provides a dependable and secure channel for fluid or gas transfer, reducing the chance of leakage. Steel tube, on the other hand, has a little larger potential for leaks owing to its welded connections if the welding is not done properly or if the tube is subjected to extreme stress or corrosion.
Structural Integrity: Steel pipe being a solid cylindrical construction has superior structural integrity. It is less likely to collapse under pressure or load-bearing circumstances. Steel tubes on the other hand with their welded connections may be more prone to collapse if subjected to high load or an unsuitable structural design.
Conclusion
In conclusion, steel pipes and steel tubes have distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. Steel pipes are primarily used for fluid and gas transportation and are manufactured as a single piece of metal. They come in various diameters and offer reliable performance and durability. On the other hand, steel tubes have a broader range of applications, thanks to their different shapes and sizes. They are often utilized in structural projects where strength and versatility are crucial. While pipes generally have higher structural integrity, tubes provide flexibility and can be customized to meet specific requirements. The choice between steel pipes and steel tubes depends on factors such as intended use, cost considerations, and the specific demands of the project at hand. Both options play vital roles in various industries, contributing to infrastructure development, manufacturing processes, and construction projects.