Laser Welding or Laser Beam Welding is a process used for melting the materials that are fused together when they cool down with the help of a concentrated heat source in the form of a laser. While running narrow and deep welds for thicker materials, it can weld thin materials at rapid welding speeds which is why this process is versatile.
While considering the cost of laser welding equipment to the other traditional welding processes, laser beam welding is much more expensive than others. However the operating of laser beam welding is lower, as it does not necessarily require additional filler material and post-processing.
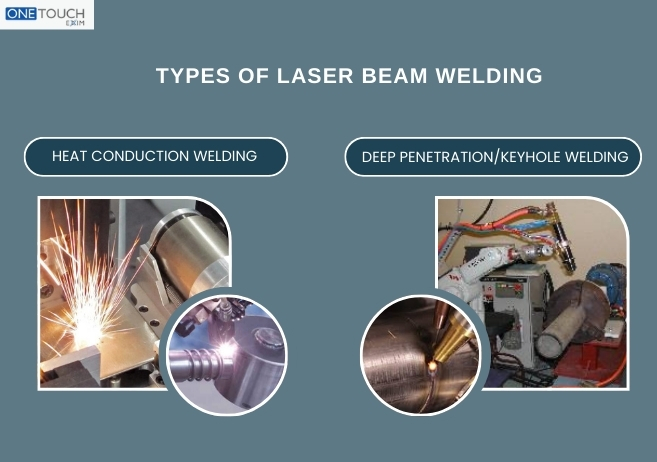
Types of Laser Beam Welding
There are mainly two types of laser beam welding. Both have unique operating principles to perform for specific applications. What determines interaction with the material is the power density of the laser beam.
Heat Conduction Welding:
According to this method. A focused laser beam is used to melt the surface of the base materials. When the joint of these metals solidifies, a smooth and precise weld seam is produced. The quality of this weld is outstanding. Welds performed while using this method do not need any additional finishing. By the heat conduction, the energy enters into the weld zone. This limits the depth of welding thus this process is fabulous for joining the thin materials. The welding process is used for the visible weld seams which are aesthetically pleasing.
There are mainly two subcategories of heat conduction welding:
- Direct heating – The power is directly applied to the surface of the metals.
- Energy transmission – Absorbing ink is applied to the joint, soaking up the laser beam’s energy.
Deep Penetration/Keyhole Welding
While performing the process in keyhole welding/ deep penetration mode, the deep and narrow welds must be created with uniform structure. While working on metals the power density of about 1 MW per square centimeter should be applied. It vaporizes but does not melt the metal, creating a narrow vapor-filled cavity.
This is called the keyhole cavity or vapor capillary. It is filled with molten metal as the laser beam advances through the workpiece. The formation and the distortion of a heat-affected zone are kept to a minimum.
How Does Laser Beam Welding Work?
Using a concentrated, collimated, high-intensity light beam, laser welding is a process that melts and fuses metal components, occasionally adding extra material from a filler rod. The procedure produces laser light, which is subsequently directed into an optical head or collimator. It is then directed towards the metal parts’ junction, where it results in a limited melt pool and intensely confined heat buildup.
Usually, a solid-state, fiber, or CO2 laser—each with certain benefits—generates the laser welding beam. The metal melts at the focus point of the beam, creating a small pool into which the filler rod can be melted as needed. The joint’s surface is then traversed by the laser beam. As a result, the pool’s leading edge melts and its fused, molten trailing edge cools and solidifies. When a weld is successful, the cooled metal fuses to both pieces almost equally and does not oxidize.
What are the Advantages of Laser Beam Welding?
The laser welding has a wide range of advantages as compared to the other methods like TIG, MIG, and Arc Welding. Some of the advantages of laser welding are as follows:
- The Heat Affected Zone is smaller. The energy of the laser beam is primarily focused in every small area and moved as soon as possible. There is no necessary heat input. The areas that should be heated are heated with this level of control and precision.
- Parts maintain better mechanical properties. Because of the low heat input, this is less part warping and heat distortion. In the step that is used in the other welding methods, excess heat degrades mechanical properties and often creates the need for straightening is not required.
- The small components can be welded because of their high level of precision. This is mainly relevant for tab connections, electronic components, and similar applications.
- The laser welding is faster than other processes. The fiber technology and industrial lasers are easily operated at thousands of watts, which is more than enough to meet the production requirements.
- Laser welding is easy to automate because of its factors like capabilities, remote, mineral wear and tear, and repeatability. These factors make the technology interesting for manufacturers who have trouble finding specialized welders.
What are the Disadvantages of Laser Welding?
There are not many disadvantages of laser welding but the disadvantages should be considered as important. Some of them are as follows:
- Laser safety is a major issue while performing a weld. The reflection of the laser beam can cause injuries such as eye injuries and skin burns also fire hazards.
- In various applications, it can cause headaches. Structures and large parts such as ships can be difficult to contain in an enclosure.
- Handheld devices can be dangerous for operators who need to wear PPE and follow laser safety control measures.
- Laser optics are quite soft or delicate and can easily be damaged while performing the weld.
Conclusion
Laser beam welding is a highly precise and efficient welding process that utilizes a focused laser beam to join two materials together. By directing the intense energy of a laser beam onto the workpiece, the material is melted and fused together with minimal heat-affected zone and distortion. This process offers numerous advantages such as high welding speed, narrow weld seams, and the ability to weld a wide range of materials. Overall laser beam welding is a sophisticated and versatile technology that plays a vital role in various industries.