Stainless steel vs carbon steel is generally used substances with unique properties and applications. While stainless steel offers wonderful corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, carbon steel excels in strength and sturdiness. In this blog, we will find out the variations among these types of steel, their benefits, applications, and the manner of picking the right one for specific requirements. By understanding their exceptional qualities, you can make informed choices at the same time as choosing appropriate steel according to your requirements.
Comparing Stainless Steel with Carbon Steel
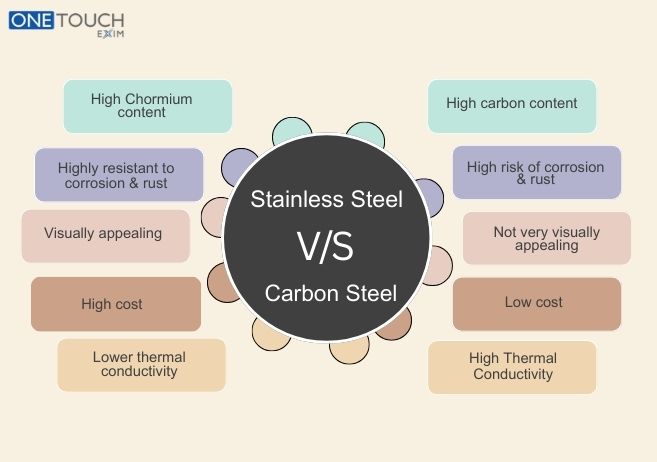
The major difference between stainless steel and carbon steel is their corrosion resistance. Because stainless steel includes chromium, it creates a thin layer of chromium oxide at the surface, which protects it from rust and other kinds of corrosion. Carbon steel, alternatively, lacks this shielding layer, which makes it more prone to corrosion. Carbon steel is different and stronger than stainless steel.
Carbon steel’s strength and hardness are obtained from its carbon content material. However, the presence of carbon material makes it to be greater brittle than stainless steel. Carbon steel is harder and stronger, but it is also more liable to breaking while bent or formed excessively. Generally, stainless steel is more costly than carbon steel.
Benefits of Stainless Steel
Stainless steel has numerous advantages. When chromium is added to stainless steel, it forms a skinny protecting film that resists rust and corrosion. It can resist high temperatures, making it beneficial for temperature-sensitive applications. Stainless steel is light weighted and strongest steel, and it can bear heavy loads. Additionally, stainless steel requires no maintenance and is certainly recyclable, which is environmentally friendly.
Benefits of Carbon Steel
Carbon steel has its own set of benefits. It can withstand excessive stresses and effects, making it appropriate for applications that require power and durability. Carbon steel is normally less costly to fabricate and buy in comparison to other steel forms. Like stainless steel, it is also 100% recyclable and can be used a couple of times without compromising its quality and strength. Additionally, carbon steel is flexible and can be shaped easily, machined, or welded into diverse bureaucracies.
Stainless Steel Applications
The application of stainless steel is found in numerous industries where corrosion-resistant steel is essential. Its visually appealing properties also make it suitable for decorative products. Some common activities that consist of the following stainless steel:
a). Kitchen Appliances
Stainless steel is normally used in the construction of kitchen appliances which includes refrigerators, ovens, dishwashers, etc.
b). Medical Devices
Due to its sterilization properties, stainless steel is extensively used in the manufacturing of clinical devices like scalpels, clamps, needles, etc.
c). Architectural Components
Stainless steel is used to create architectural properties and structures, consisting of handrails, doors, and window frames, etc.
d). Aerospace and Defense
The power and sturdiness make the stainless steel perfect for building aircraft companies and different protection-related equipment.
e). Others
Stainless steel is used in the production of exhaust systems and trim components.
Carbon Steel Applications
Carbon steel is preferred in applications that require strength and hardness. Some common applications of carbon steel consist of the following:
a). Construction
Carbon steel is generally used in construction work like bridges, buildings, and structural components due to its hard strength.
b). Automotive
It finds applications in the manufacturing of automotive parts, along with engines, transmissions, and wheels.
c). Industrial Machinery
Carbon steel is used in Industrial work like the manufacturing of boilers, tanks, and different business utilities.
d). Machine Parts
Carbon steel is generally easy to machine unless it is heat-treated to high-tensile or wear-resistant levels. It is typically used for manufacturing gears, and bearings, and comes, thanks to its strength and durability.
e). Cutting Tools
Carbon steel is used for making knives and saws, because of its ability to keep a pointy and sharpness part.
Choosing the Right Type of Steel
Selecting the appropriate steel type relies upon the particular necessities of your application. If high corrosion resistance is vital, stainless steel is the preferred choice. For applications that demand strength and hardness, carbon steel is recommended. If budget is a problem, carbon steel is a cost-effective option as it is normally lower in price than stainless steel. The resistance of stainless steel to corrosion makes it appropriate for things uncovered to moisture or corrosive environments.
Final Verdict on Stainless Steel and Carbon Steel
Comparing low-carbon steel to stainless steel it offers extensive improvements in strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance. High-carbon steel can rival or even surpass stainless steel in terms of power, however, it’s far more utilized in specific niche applications. Unlike carbon steel, stainless steel flourishes in corrosive or humid environments without oxidation. However, carbon steel is lower in price and highly applicable for large structural components including tubes, beams, and sheet steel.
Conclusion
In conclusion, stainless steel and carbon steel have their own advantages and are appropriate for extraordinary purposes. Stainless steel stands out with its corrosion resistance, temperature tolerance, and visual appeal, making it perfect for applications in various industries. On the other hand, carbon steel’s strength, durability, and price effectiveness make it a preferred choice for structural components and packages requiring high-impact resistance. Ultimately, the choice between stainless steel and carbon steel relies upon the requirements of your projects, thinking about elements such as corrosion resistance, strength, budget, and environmental issues.