Most people are unsure whether stainless steel is magnetic or non magnetic stainless steel. According to their properties, some stainless steel varieties are magnetic while others aren’t. In simple terms, we can say metals that are attracted by magnets are magnetic metals, and those that aren’t attracted by magnets are non-magnetic metals. Magnetic stainless steel has more chromium and molybdenum, as well as Non-Magnetic steel has better corrosion resistance than the common magnetic grade. The stainless steel grade atoms are lined up in a crystal structure. Magnetic materials contain iron and come down to the microstructure of steel. And non-magnetic substances contain a high amount of austenitic. Both are widely used for industrial purposes.
Now, let’s talk in brief about the differences between magnetic and non-magnetic stainless steel and their types. We hope this blog will be useful for understanding the difference between magnetic and non-magnetic stainless steel.
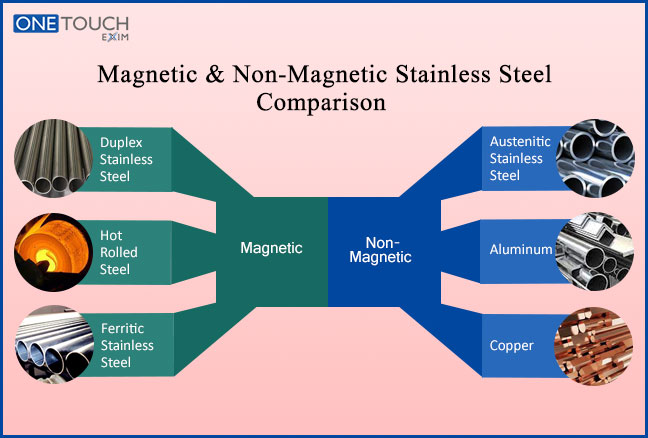
Magnetic Stainless Steel And Their Types
Stainless steel is a unique alloy. The stainless steel magnetic is used in a testing process to verify the composition of steel. Magnetic stainless steels are those steels that are not free from the magnetic test. There are some magnetic stainless steel types discussed below:
Duplex Stainless Steel
It is one of the most recent alloys that is steel magnetic, it offers easy fabrication, excellent balance of corrosion resistance, and price savings, because of the non-appearance of nickel in its composition. It has a two-phase microstructure of ferrite grains and austenite and is mainly designed to provide better corrosion resistance, chloride stress corrosion, chloride pitting corrosion, and also stainless steels such as type 304 (contains 8% nickel and 18% chromium) and 316 (contains 10% nickel and 2% molybdenum).
Ferritic Stainless Steel
Ferritic Stainless Steel is also a family of stainless steel, this is the most cost-effective family of stainless steel. It has magnetic properties due to the alloy’s large ferrite composition. Although, this is Stainless Steel magnetic, by contrast, is arranged as a body-centered (bcc) lattice. Atoms are arranged in the corners of the cube and another single one is located in the center of the cube. Most likely Bcc crystal is made up of Silicon, chromium, and molybdenum.
Hot Rolled Steel
This stainless steel has roll pressed at extreme temperatures, which makes the steel easier to form, shows the results of the product, and is easy to work. After this process, hot-rolled steel shrinks slightly as it cools. It is ideal for stainless magnets where tolerances and precise shapes are not as important. Mostly used in construction and welding trades for making I-beams and railroad tracks. It has extreme tensile and yield strength.
Non-Magnetic Stainless Steel And Their Types
Magnetic testing of stainless steel is not reliable, as its effectiveness is due to the composition of stainless steel. It consists of austenitic, aluminum, and copper, hence recognized as stainless steel. There is some stainless steel that has less or lacks magnetic properties in its composition. Some of the types of non-magnetic stainless steel include the following:
Austenitic Stainless Steel
Austenitic stainless steels contain nickel and that is non magnetic steel. If the alloy is austenitic crystal structure in nature, then it’s non-magnetic. Rich in strength, durability, and corrosion resistance, magnetic steel. This stainless steel is environmental friendly, easy to produce, clean, and maintain. Alloy is used as a structural component in present and future nuclear reactor systems. Widely used in many industries including automotive, aerospace, industrial applications, and medical.
Aluminum
It is a non-magnetic metal that represents nature similar to lithium and magnesium. Under normal conditions, the nature of aluminium has no visibly magnetic steel, while on the other hand, high enough magnetic fields-most matter will show some magnetic attraction. It is useful in many ways because of machinability, strength, heat treatability, corrosion resistance, and weldability. These uses of this magnetic steel include aircraft parts, decorative hardware, brakes, marine fitting & hardware, electrical components, hydraulic pistons, pins, bicycle frames, and valves.
Copper
It is a non-magnetic metal; hence, it lacks magnetic properties. It is one of the few metals that has natural color. It is a reddish-gold metal combined with bronze alloy. It has high electrical because of the electrical conductivity. It is usually used to make coins, and it is a good conductor of heat and electricity. It can also show interactions with magnets. It, however does not react with water, but slowly reacts with atmospheric oxygen and protects the underlying metal from corrosion.
Magnetic Steel vs Non-Magnetic Stainless Steel
| Property | Magnetic Steel | Non-Magnetic Stainless Steel |
| Magnetism | Magnetic | Non-magnetic |
| Corrosion resistance | Varies based on steel grade | Excellent |
| Hardness | Can be hardened | Generally not hardened |
| Machinability | May require special techniques | Easy to machine |
| Weldability | Can be welded with proper care | Easy to weld |
| Formability | Can be formed into complex shapes | Good formability |
| Cost | May be less expensive | Generally more expensive |
| Applications | Used in magnetic applications | Used in non-magnetic applications, such as food processing and medical equipment. |
Conclusion
In conclusion,stainless steel magnetic or not depends on its composition and crystal structure. Non-magnetic stainless steel is a combination of iron, chromium, manganese, nickel and other elements, which work together to form an alloy with low magnetic permeability. For the magnets that stick to stainless steel, the alloy’s crystal structure must be arranged in a ferritic or martensitic structure. And also the alloy must have iron in it. On the other hand, austenitic stainless steel contains nickel and if the alloy has a crystal structure of austenitic, then it’s not magnetic. Simply, duplex, ferritic & hot rolled steel is magnetic stainless steel and austenitic, aluminium, and copper is non-magnetic stainless steel.